Target selection.
This is a 3 stage process. 1st, the master data frame is pivoted by target using proteinNameC as target descriptor. The target pivoted data frame contains the following records:
| proteinNameC | Name of the protein target |
| target_description | Type of target |
| proteinType | Type of protein |
| GiProteinNumber | Gi code for protein number. To enable join with biosystems |
| Avg(chemblActivityScoreC) for N | Average potency recorded for all assays in ChemBl for compounds predicted inactive by our prediction model |
| Avg(chemblActivityScoreC) for Y | Average potency recorded for all assays in ChemBl for compounds predicted active by our prediction model |
| Count(chemblActivityScoreC) for N | Number of times that the compound has been inactive upon each ChemBl protein target |
| Count(chemblActivityScoreC) for Y | Number of times that the compound has been active upon each ChemBl protein target |
| targetClass | Protein family of proteinNameC protein |
| proteinClassDescription | Class to which protein NameC protein belongs |
| organismC | Organism to which protein NameC protein belongs |
| AvgChemblActivityScoreC | Average potency for all ChemBl assays |
| CountChemblActivityScoreC | Number of records for a particular proteinNameC protein in ChemBl database |
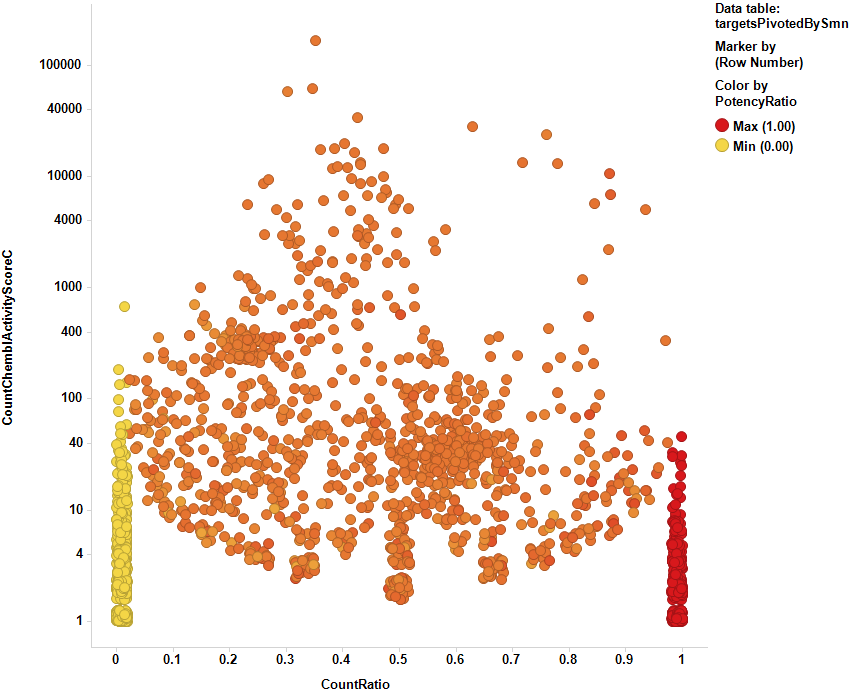
| CountRatio | Number of times in which the protein target has been active divided by the total number of records of a particular target |
| PotencyRatio | Average potency for a particular proteinNameC active records divided by total records of the sample protein |
A custom view offers this aspect, each dot corresponding to an individual target.
At this moment, the most impactful targets can be selected picking the top right zone of the graph, where the targets with the highest activity count ratio (actives vs total) with the highest number of occurrences lie.
In a second step, the master file is processed through the apriori (arules) algorithm once the key parameters are converted to factors. Redundancies are removed and rules are sorted by lift for further visualization in R or SpotFire. When general rules are displayed, targets are isolated for matching with the pivoted targets table. Alternatively, if other DB variable is of interest for the analysis, as assay type or assay name, this can be isolated as well, although this should match with its own pivoted (by assay type or name) table.