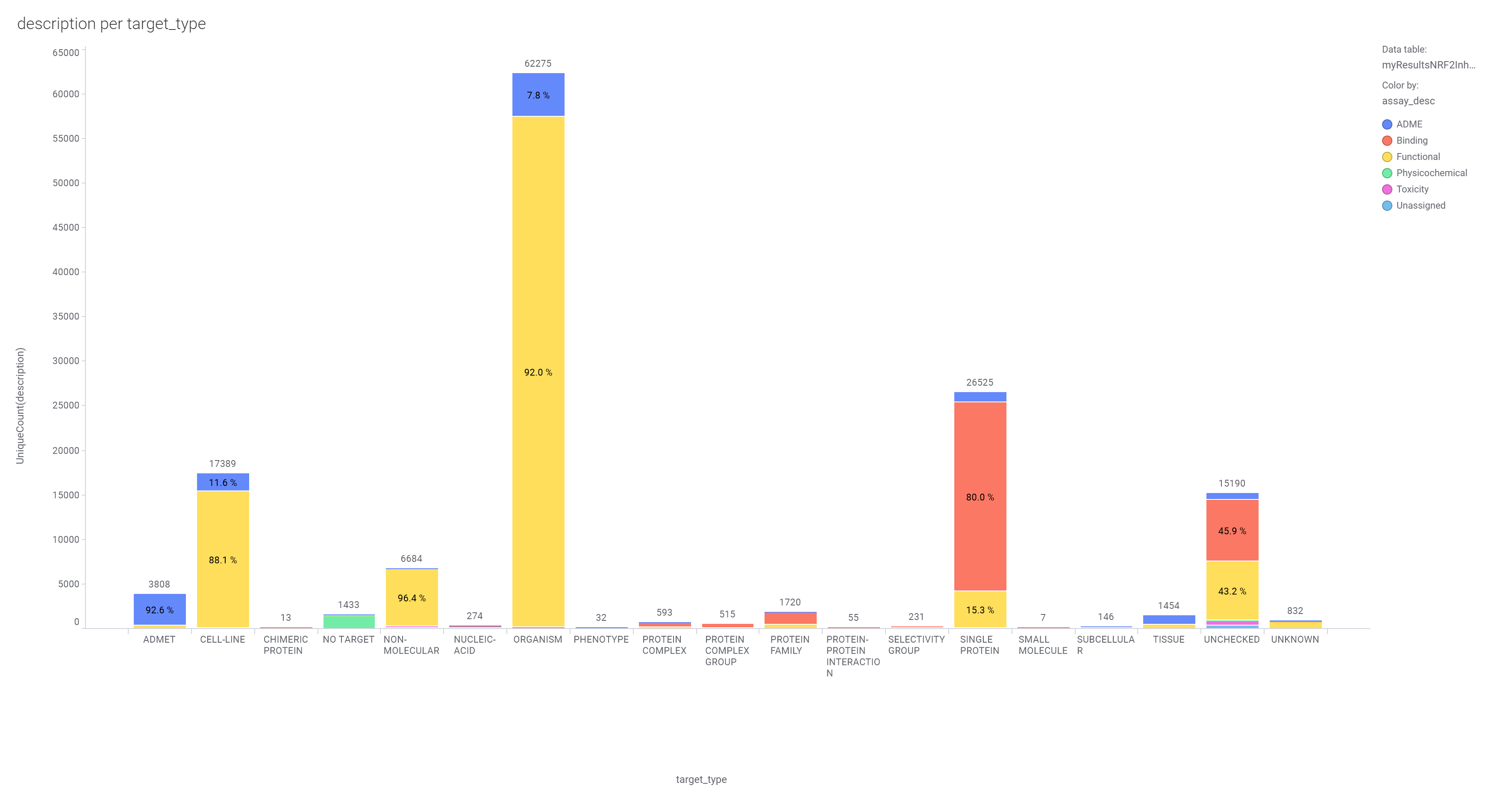
drTarget Machine Learning models to identify potential COVID-19 & SARS inhibitors from public repositories.
This site contains free downloadable contents with the aim to support whoever may be interested in testing potential SARS-type viral inhibitors. No experimental evidence has been generated. These potential inhibitors come from a predictive machine learning exercise on PUBCHEM and ChEMBL DBs.
Zip folder contains dwar and txt files with 21kcompounds identified as SARS active in chembl. There is a second pair of txt and dwar files containing only the ChEMBL molecules with drug name.
Data sources.
Although There are no data in public repositories regarding antiviral assays for COV-19, both ChEMBL and PUBCHEM DBs store a good amount of records of molecules interacting with SARS proteases and inhibiting virus proliferation in diverse phenotypic assays. Click on the links below to access to the sources of these studies.
qHTS of Yeast-based Assay for SARS-CoV PLP
Data modelling.
Data from described sources have been pooled together and a common SARS score has been generated based in their respective activities upon different assays. The common SARS score takes into account several activity records to configure a combined SARS score common for all stored assays (PCHEM score, pXC50, max inhibition, activity in secondary assays, area under the compound concentration-response curve -AUC- and others). The activities of several SARS protease inhibitors recently assayed for COVID-19 growth inhibition in cell cultures and humans and reported have also been included and a common SARS score has been calculated accordingly.
About 300k molecules have a record in at least one SARS assay, and more than 4M records in the ChEMBL DB associated to >130k assays carried out on 4700 different protein targets and 100k phenotypic assays.
The 4M ChEMBL records have been used to create a number of machine learning models that incorporates assay, organism, protein and molecular properties. Classification and regression random forests algorithms resulted the most successful among all.

Validation results. Comparison between actual SARS scores and predicted ones. left: combined classification and regression predictions. Right: regression.
Prediction of activity.
Once the model is validated, it can be applied to the whole DB content, calculating a SARS predicted score for 1.5M compounds, finding 21k active molecules.
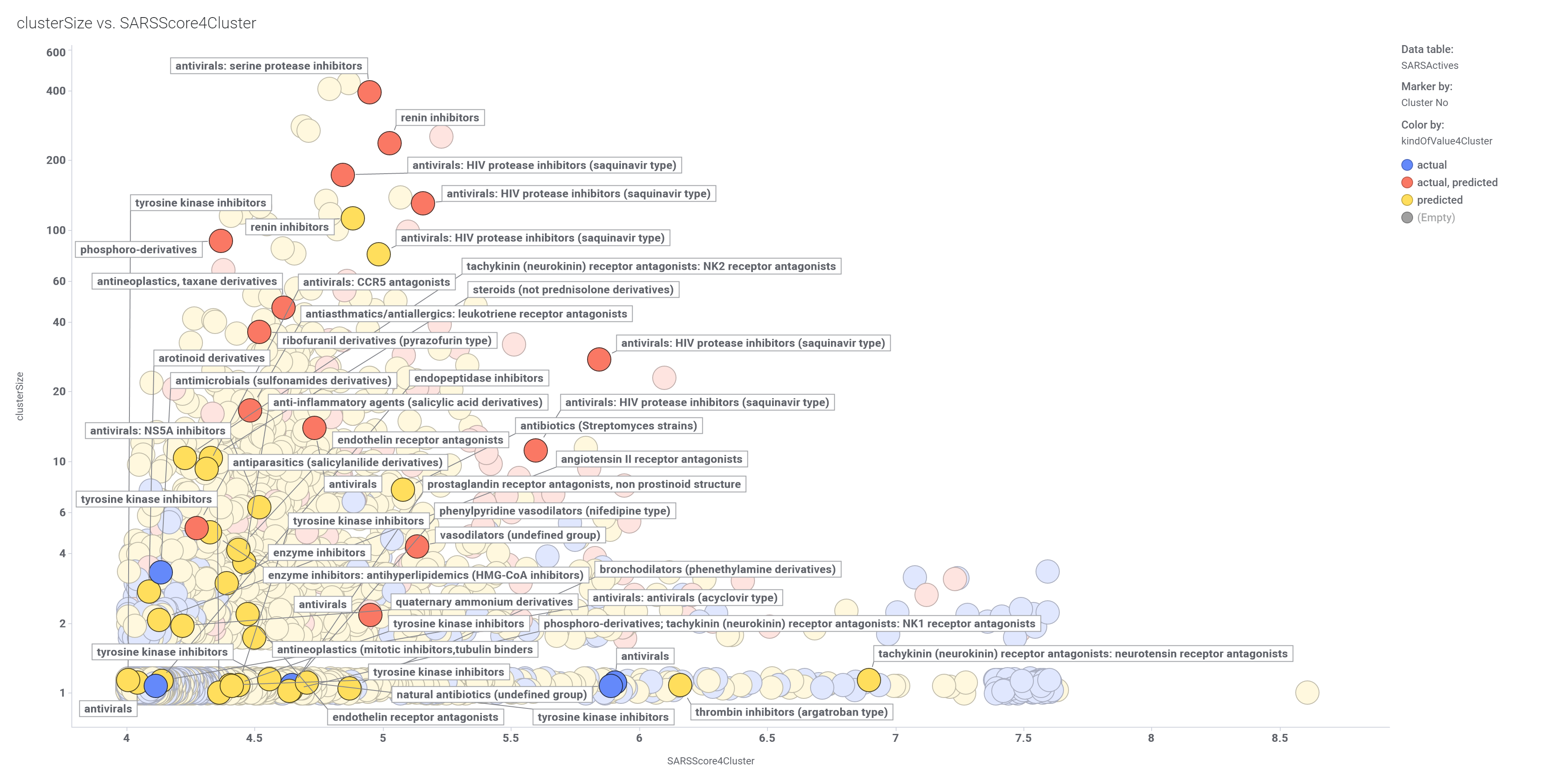
Compounds have been clustered attending to their similarity. We can now look at more interesting clusters by its average potency for SARS and the number of representatives.
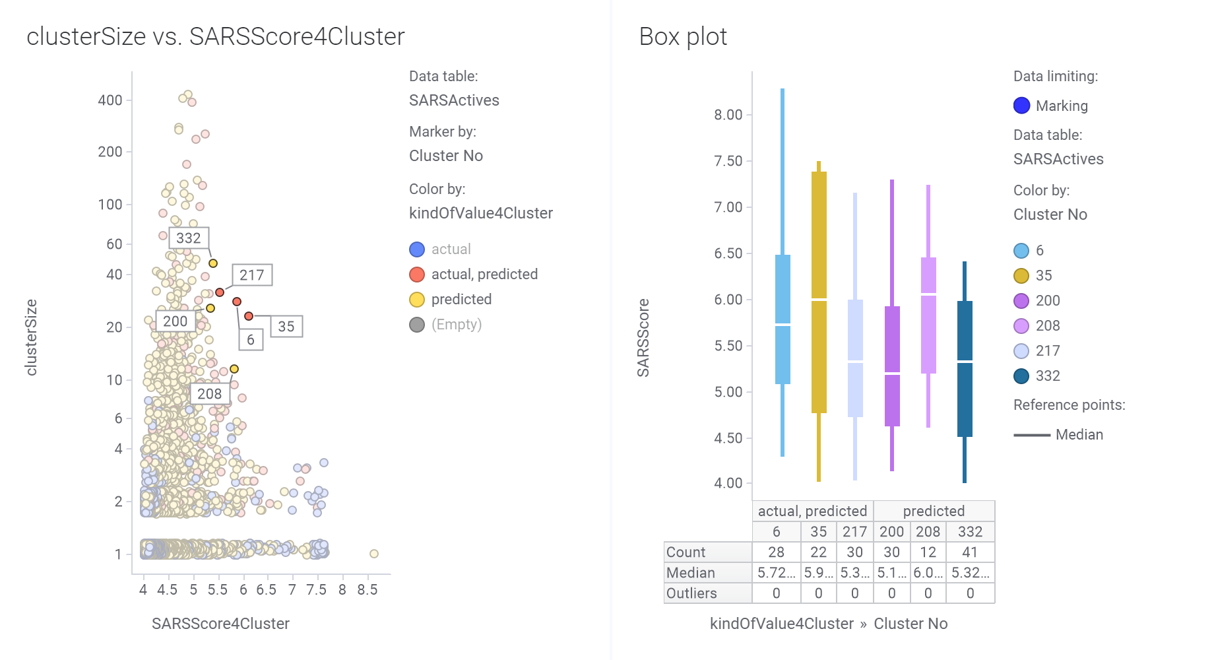
Scatter plot (left) showing potency and size distribution of classified molecules. Dot labels represent the cluster ID. Marked clusters in the left chart become represented in the box plot on the right hand side.
Some of the clusters include antiviral compounds, not only protease inhibitors…

Scatter plot (left) showing potency and size distribution of classified molecules. Dot labels represent the cluster ID. Marked clusters in the left chart become represented in the box plot on the right hand side.
And many other mechanisms of action, besides other not annotated clusters…
Some structures…
Like compounds similar to the protease inhibitor lopinavir…
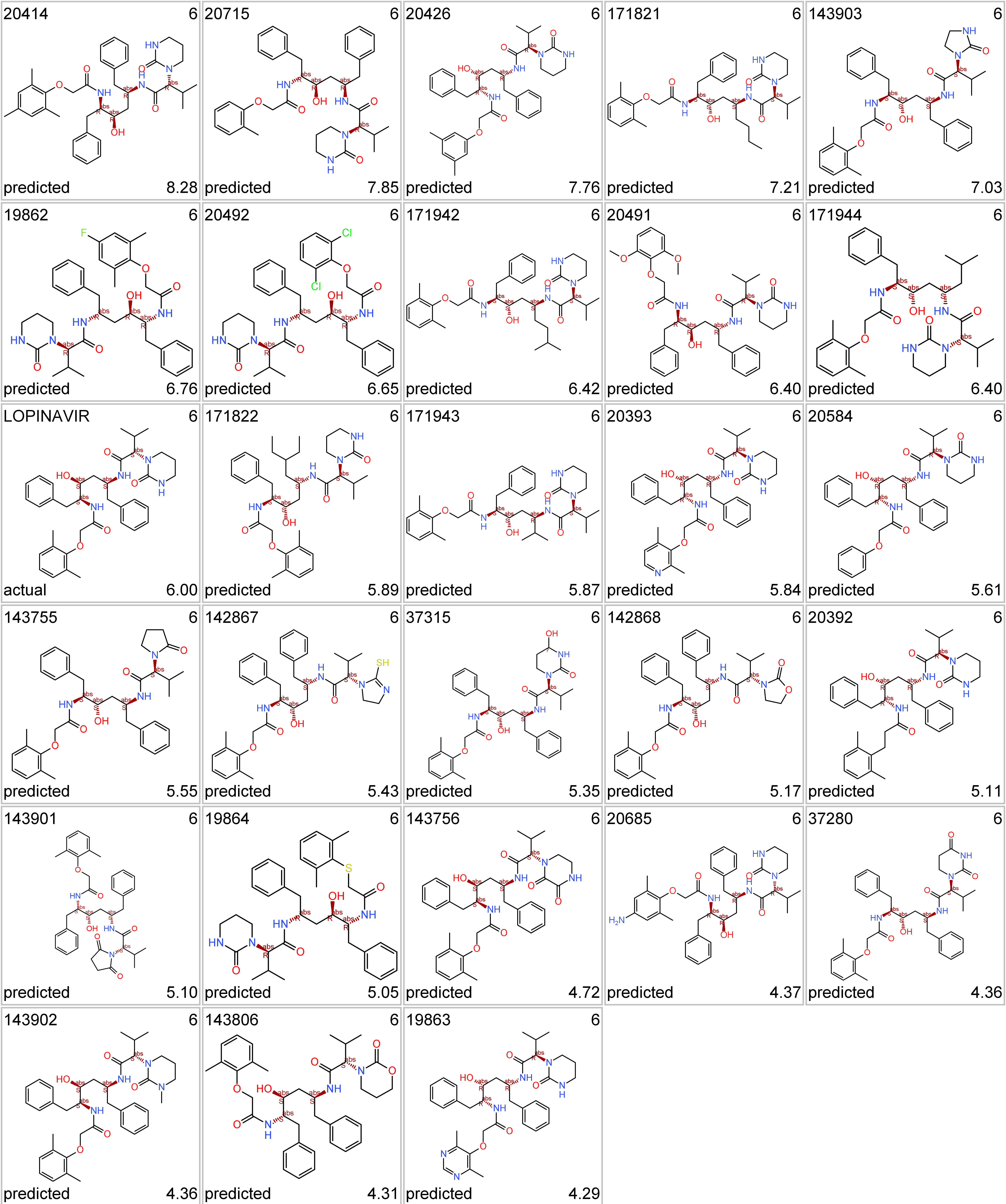
Lopinavir protease inhibitor series. Top-left, molecule name; top right: cluster_ID; bottom left: kind of value; bottom right: SARS score.
There are also natural compounds like ellagic acid, abundant in in walnuts, pecans, cranberries, raspberries, strawberries, and grapes, as well as distilled beverages. It is also found in peaches and pomegranates (wikipedia).
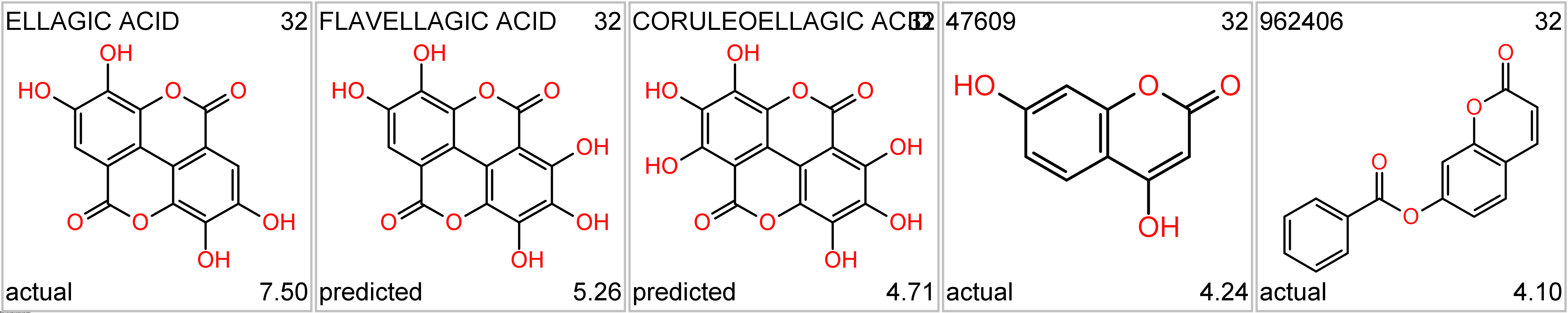
Ellagic acid series. Top-left, molecule name; top right: cluster_ID; bottom left: kind of value; bottom right: SARS score.
Tricetin a flavone, a type of flavonoid. It is a rare aglycone found in the pollen of members of the Myrtaceae, subfamily Leptospermoideae, such as Eucalyptus globulus (wikipedia).
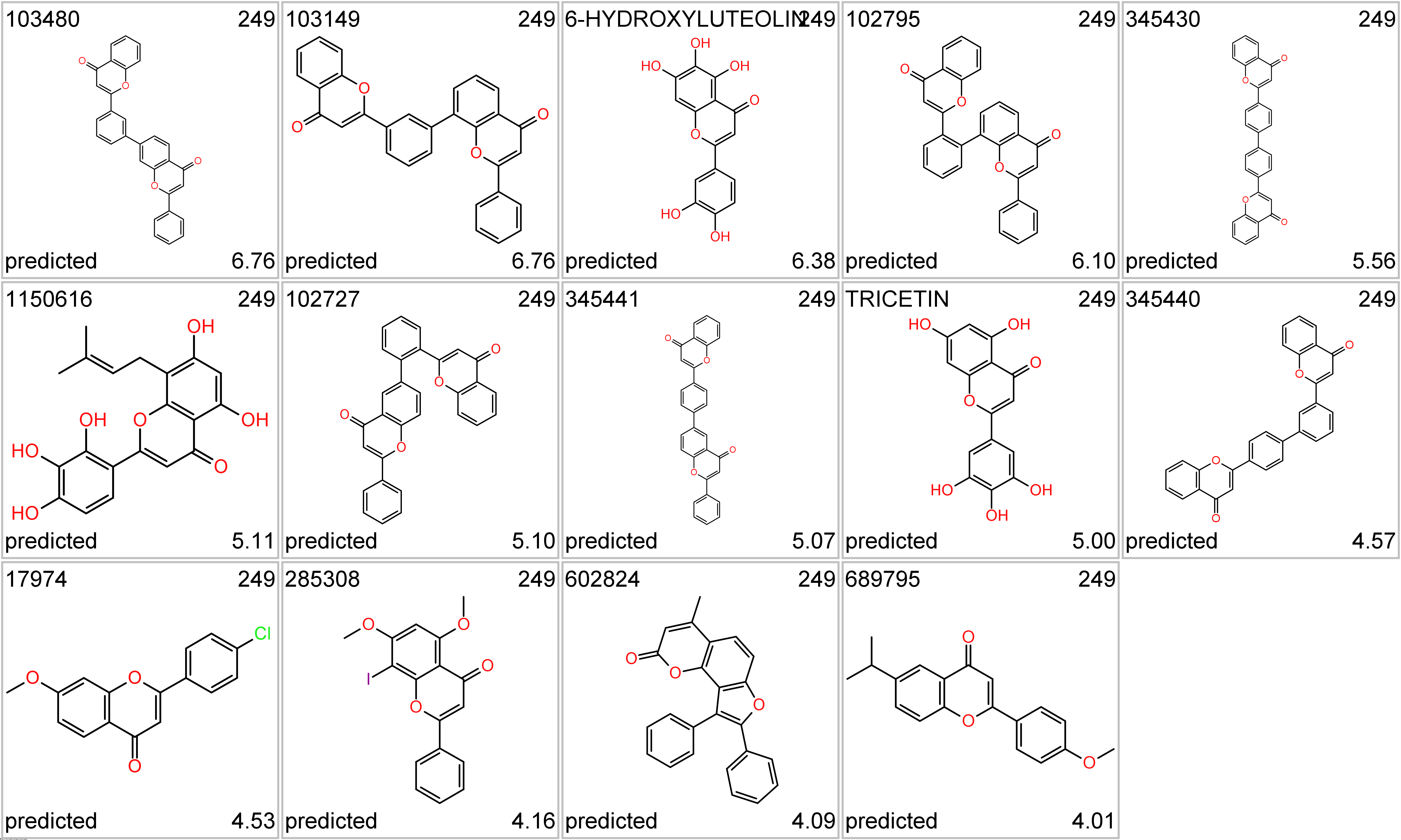
Tricetin series. Top-left, molecule name; top right: cluster_ID; bottom left: kind of value; bottom right: SARS score.