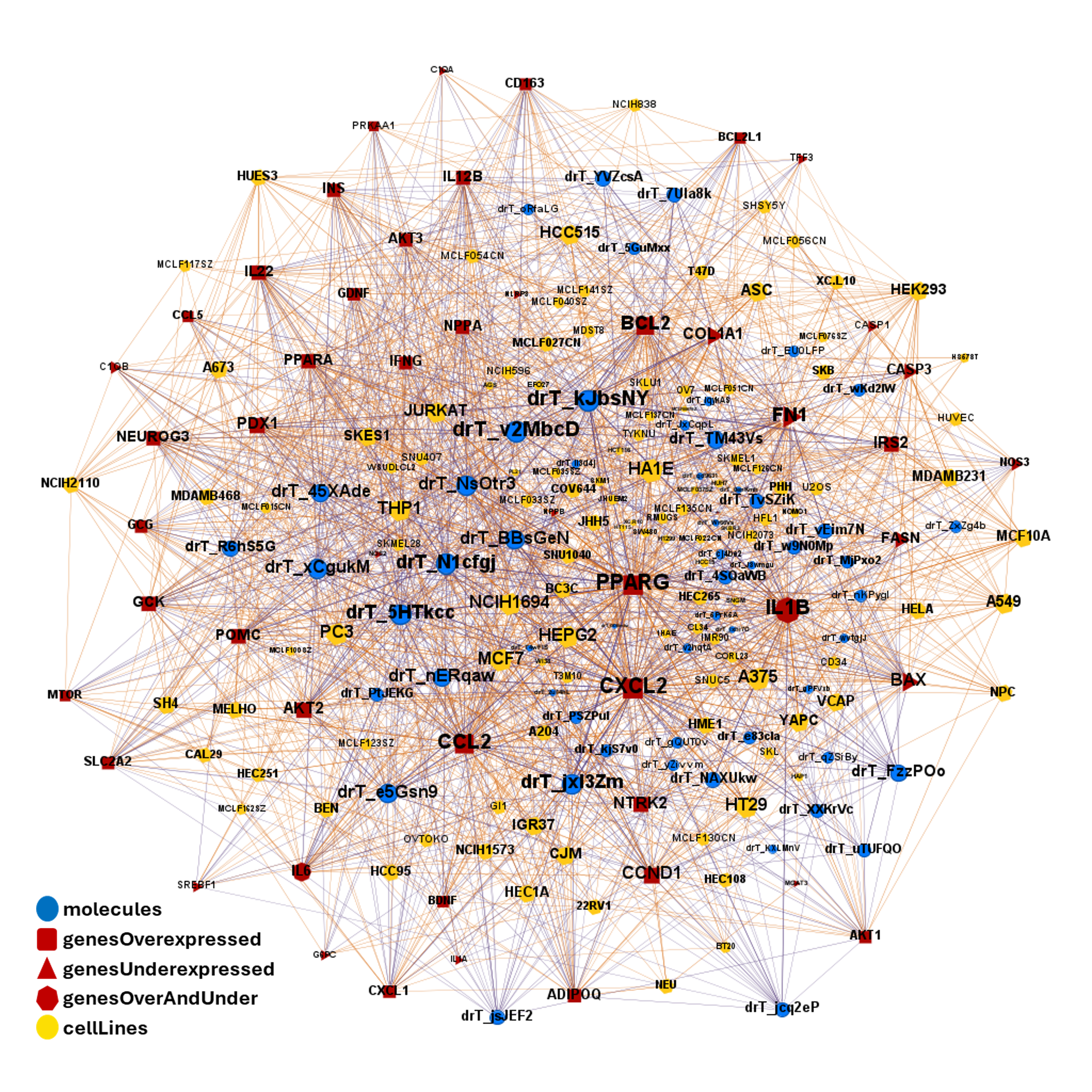
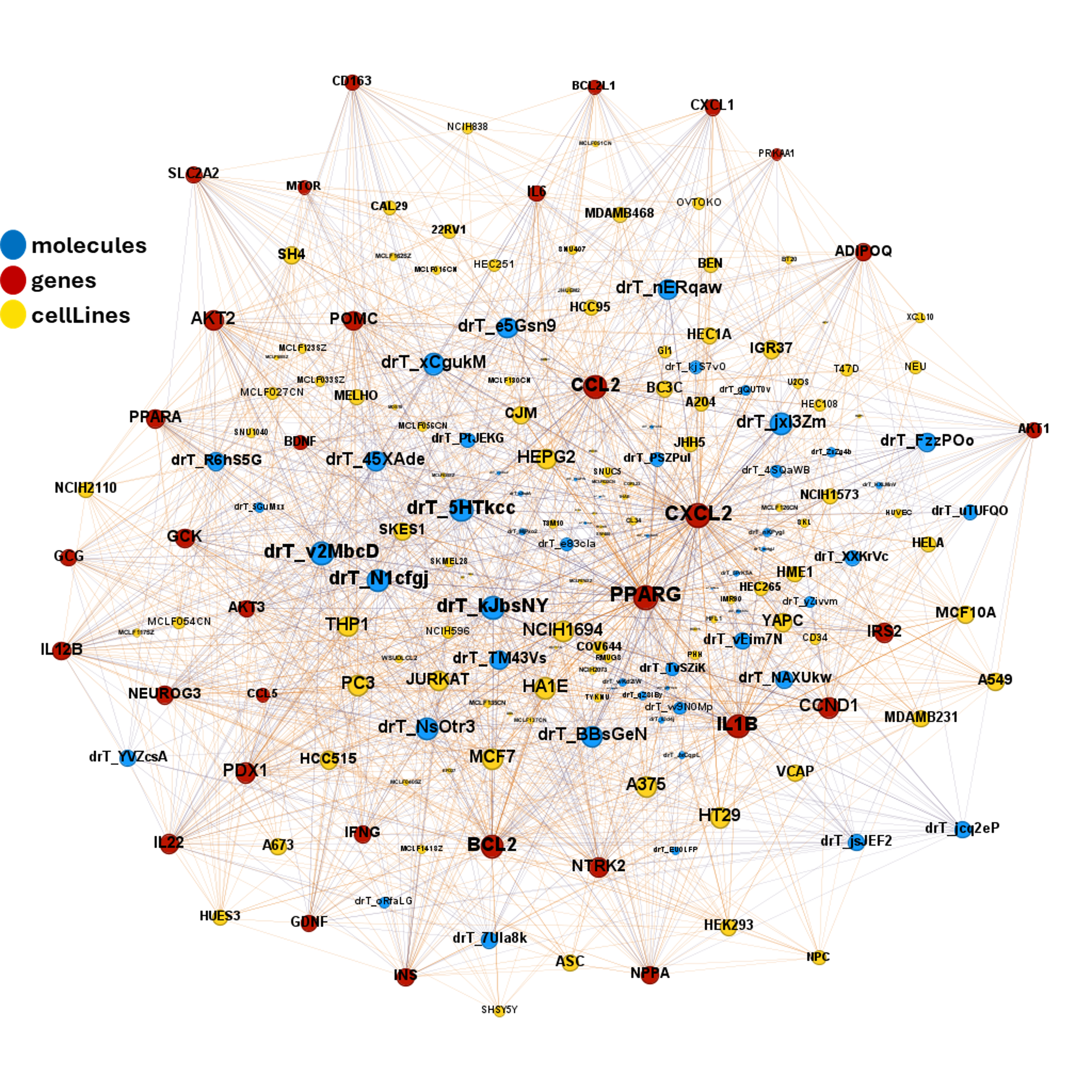
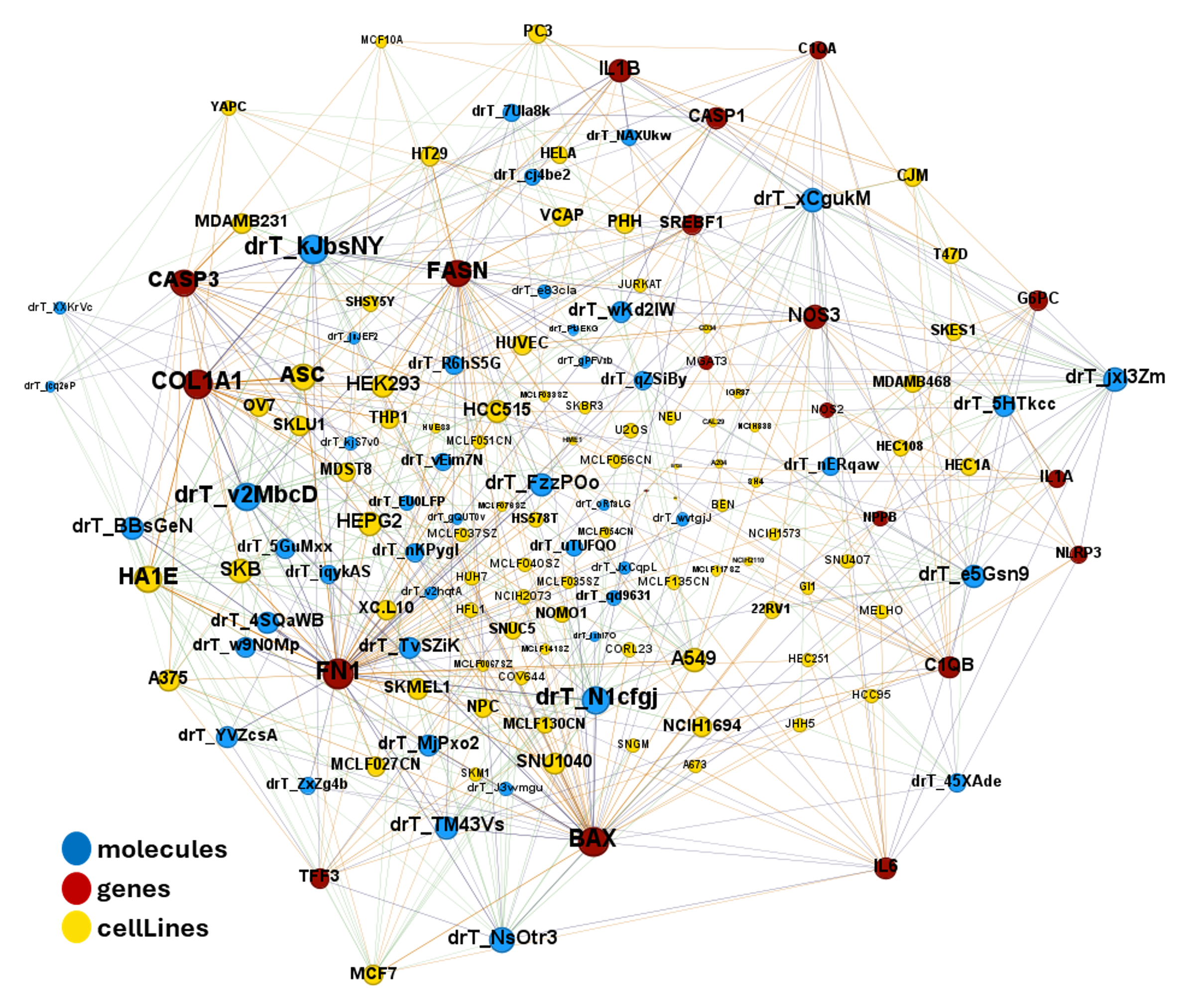
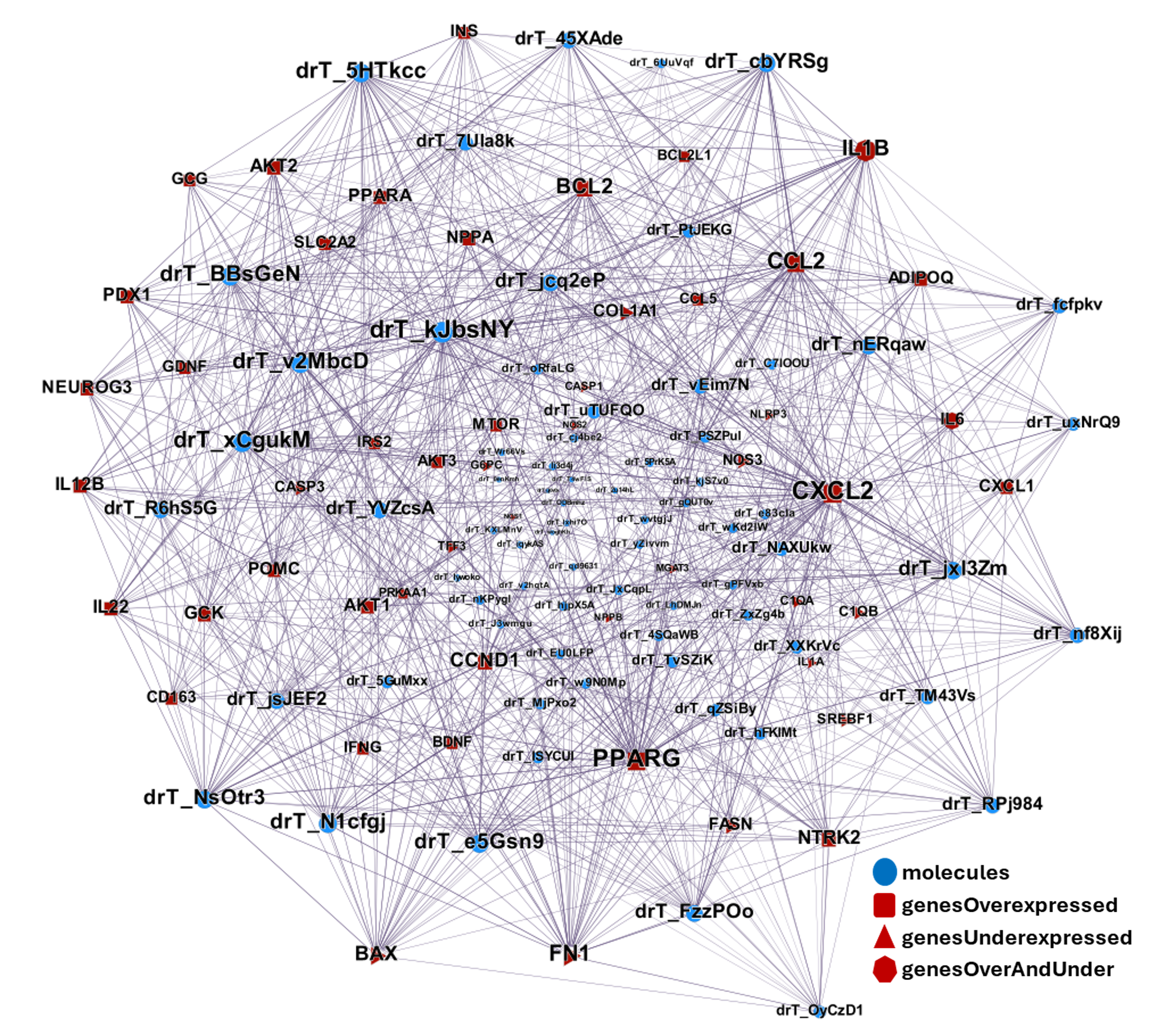
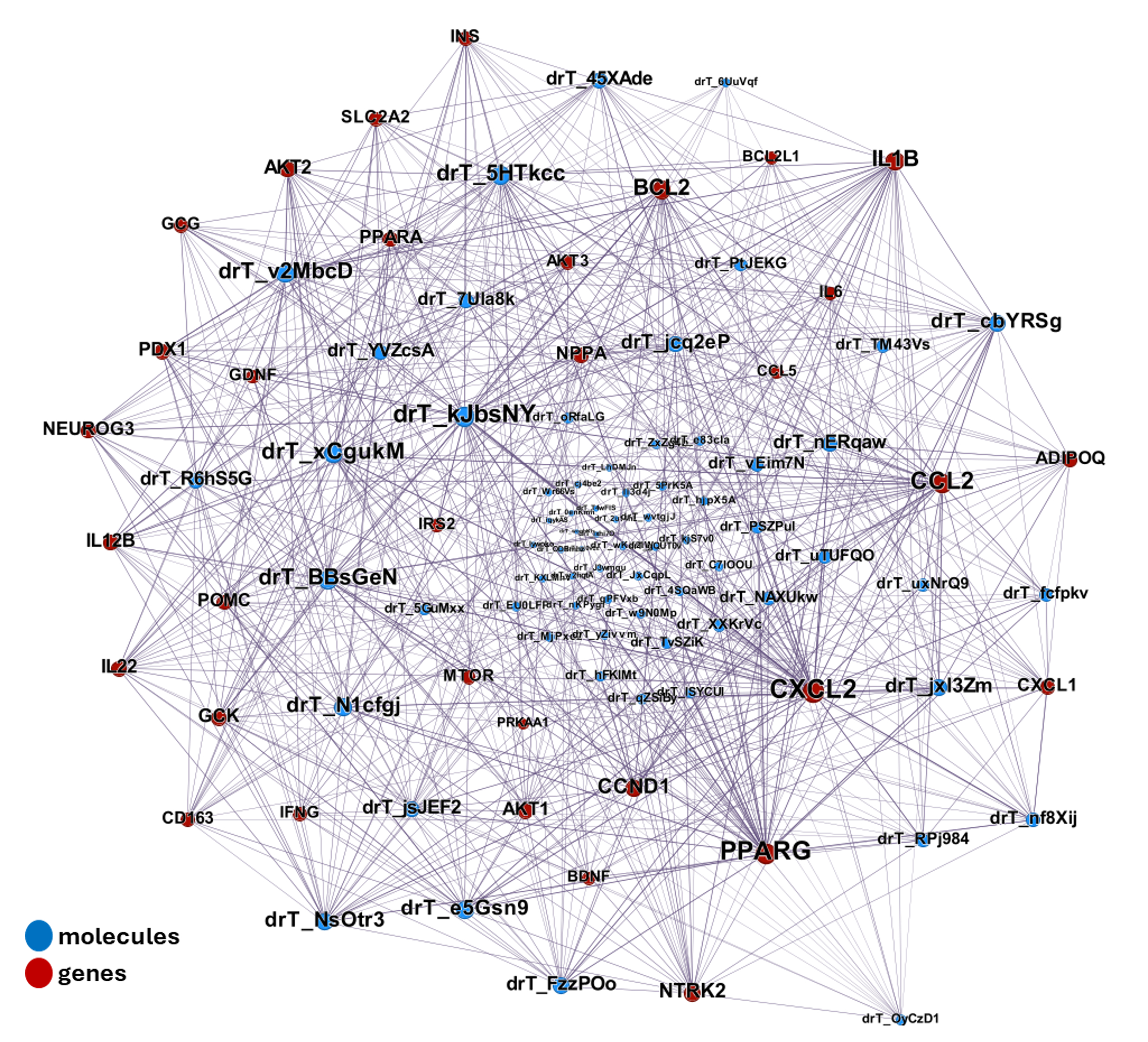
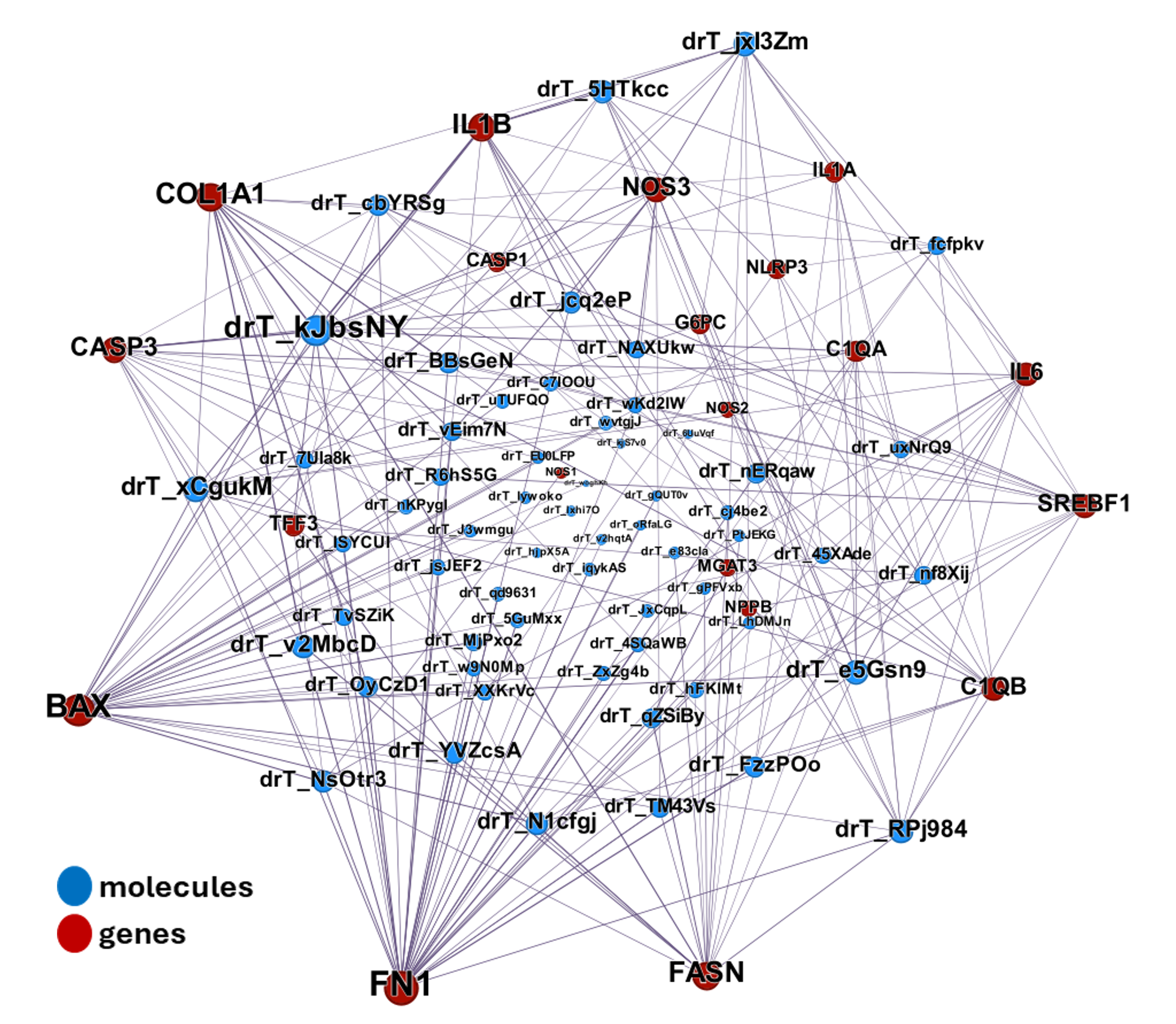
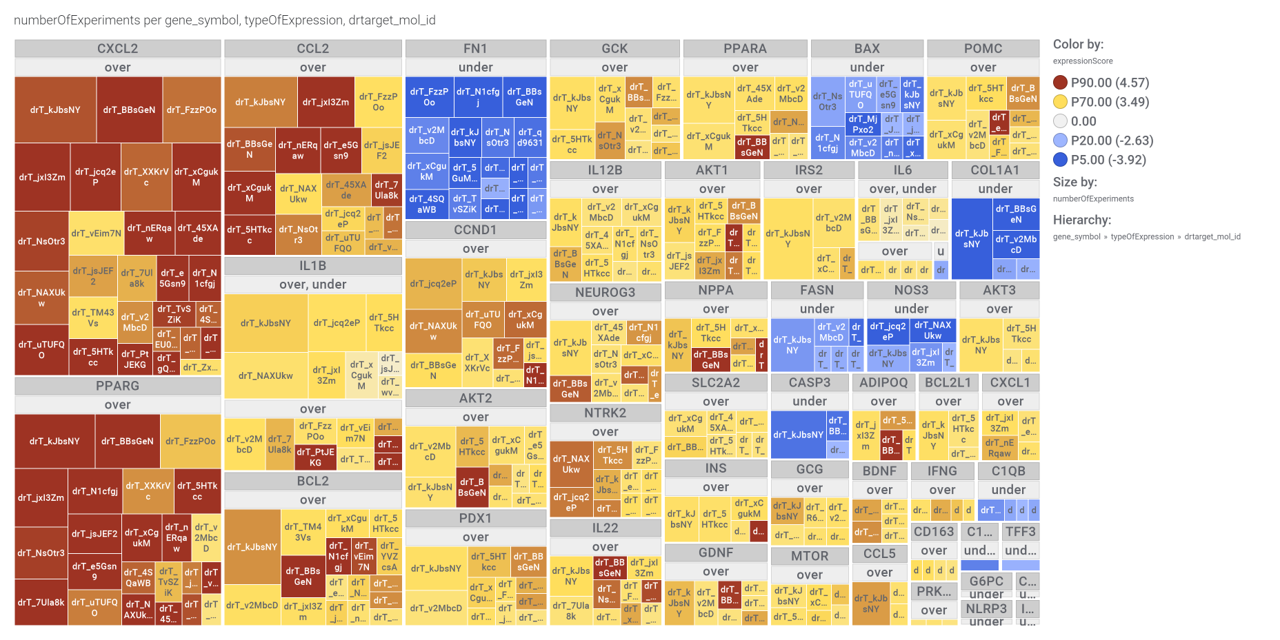
| ADIPOQ | adiponectin | increase | adipocytes | Exendin-4, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, directly induces adiponectin expression through protein kinase A pathway and prevents inflammatory adipokine expression | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.10.015 |
| AKT1 | AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 | increase | neurogenesis | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: A Focus on Neurodegenerative Diseases | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6813233/ |
| AKT2 | AKT serine/threonine kinase 2 | increase | neurogenesis | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: A Focus on Neurodegenerative Diseases | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6813233/ |
| AKT3 | AKT serine/threonine kinase 3 | increase | neurogenesis | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: A Focus on Neurodegenerative Diseases | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6813233/ |
| BAX | BCL2 associated X, apoptosis regulator | decrease | neurogenesis | Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor stimulation as a means of neuroprotection | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2828015/ |
| BAX | BCL2 associated X, apoptosis regulator | decrease | pancreas | Mechanisms of Action of GLP-1 in the Pancreas | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1934514/ |
| BCL2 | BCL2 apoptosis regulator | increase | neurogenesis | Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor stimulation as a means of neuroprotection | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2828015/ |
| BCL2 | BCL2 apoptosis regulator | increase | pancreas | Mechanisms of Action of GLP-1 in the Pancreas | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1934514/ |
| BCL2L1 | BCL2 like 1 | increase | neurogenesis | Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor stimulation as a means of neuroprotection | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2828015/ |
| BDNF | brain derived neurotrophic factor | increase | neurogenesis | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: A Focus on Neurodegenerative Diseases | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6813233/ |
| C1QA | Complement component 1q A | decrease | microglia | Anti-Inflammatory Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Activation in the Brain in Neurodegenerative Diseases | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9455625/ |
| C1QB | Complement component 1q B | decrease | microglia | Anti-Inflammatory Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Activation in the Brain in Neurodegenerative Diseases | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9455625/ |
| C1QC | Complement component 1q C | decrease | microglia | Anti-Inflammatory Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Activation in the Brain in Neurodegenerative Diseases | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9455625/ |
| CASP1 | caspase 1 | decrease | microglia | Anti-Inflammatory Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Activation in the Brain in Neurodegenerative Diseases | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9455625/ |
| CASP3 | caspase 3 | decrease | pancreas | Mechanisms of Action of GLP-1 in the Pancreas | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1934514/ |
| CCL2 | C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2 | increase | small intestine | GLP-1R Agonists Modulate Enteric Immune Responses Through the Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocyte GLP-1R | https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1583 |
| CCL5 | C–C Motif Chemokine Ligand 5 | increase | monocytic cell line | Effect of liraglutide on expression of inflammatory genes in type 2 diabetes | https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-97967-4 |
| CCND1 | Cyclin D1 | increase | pancreas | Activation of the GLP-1 Receptor Signalling Pathway: A Relevant Strategy to Repair a Deficient Beta-Cell Mass | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3118608/ |
| CD163 | Macrophage-Associated Antigen | increase | monocytic cell line | Effect of liraglutide on expression of inflammatory genes in type 2 diabetes | https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-97967-3 |
| COL1A1 | Collagen type I | decrease | hepatocytes, smooth muscle | Differential importance of endothelial and hematopoietic cell GLP-1Rs for cardiometabolic versus hepatic actions of semaglutide | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8663785/ |
| CXCL1 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 1 | increase | small intestine | GLP-1R Agonists Modulate Enteric Immune Responses Through the Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocyte GLP-1R | https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1584 |
| CXCL2 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2 | increase | small intestine | GLP-1R Agonists Modulate Enteric Immune Responses Through the Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocyte GLP-1R | https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1585 |
| FASN | Fatty acid synthase | decrease | hepatocytes, adipose tissue | GLP-1/GLP-1R Signaling in Regulation of Adipocyte Differentiation and Lipogenesis | https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28668964/ |
| FN1 | Fibronectin | decrease | lung | GLP-1 receptor agonist ameliorates experimental lung fibrosis | https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-74912-1 |
| G6PC | Glucose-6-phosphatase | decrease | hepatocytes | Duodenal GLP-1 signaling regulates hepatic glucose production through a PKC-?-dependent neurocircuitry | https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28182013/ |
| GCG | Proglucagon | increase | Enteroendocrine L Cells (Intestinal Epithelium) | GLP-1 receptor signaling increases PCSK1 and β cell features in human α cells | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7934853/ |
| GCK | Glucokinase | increase | pancreas | Activation of the GLP-1 Receptor Signalling Pathway: A Relevant Strategy to Repair a Deficient Beta-Cell Mass | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3118608/ |
| GDNF | glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor | increase | neurons | The neuroprotective effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: An in-depth review | https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnins.2022.970925/full |
| GLP1 | Glucagon-like peptide 1 | increase | Enteroendocrine L Cells (Intestinal Epithelium) | GLP-1 receptor signaling increases PCSK1 and β cell features in human α cells | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7934853/ |
| GLUT2 | Glucose transporter 2 | increase | pancreas | Activation of the GLP-1 Receptor Signalling Pathway: A Relevant Strategy to Repair a Deficient Beta-Cell Mass | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3118608/ |
| IFNG | interferon-? | increase | monocytic cell line | Effect of liraglutide on expression of inflammatory genes in type 2 diabetes | https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-97967-2 |
| IL12B | interleukin 12B | increase | small intestine | GLP-1R Agonists Modulate Enteric Immune Responses Through the Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocyte GLP-1R | https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1581 |
| IL1A | interleukin-1a | decrease | microglia | Anti-Inflammatory Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Activation in the Brain in Neurodegenerative Diseases | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9455625/ |
| IL1B | interleukin-1B | decrease | monocytic cell line | Effect of liraglutide on expression of inflammatory genes in type 2 diabetes | https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-97967-0 |
| IL1B | interleukin-1B | increase | small intestine | GLP-1R Agonists Modulate Enteric Immune Responses Through the Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocyte GLP-1R | https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1578 |
| IL1B | interleukin-1B | increase | hypothalamus | Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor induced suppression of food intake, and body weight is mediated by central IL-1 and IL-6 | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3791711/ |
| IL22 | interleukin 22 | increase | small intestine | GLP-1R Agonists Modulate Enteric Immune Responses Through the Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocyte GLP-1R | https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1580 |
| IL6 | interleukin 6 | increase | small intestine | GLP-1R Agonists Modulate Enteric Immune Responses Through the Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocyte GLP-1R | https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1579 |
| IL6 | interleukin 6 | increase | hypothalamus | Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor induced suppression of food intake, and body weight is mediated by central IL-1 and IL-6 | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3791711/ |
| IL6 | interleukin 6 | decrease | neurogenesis, macrophages, immune cells | Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor stimulation as a means of neuroprotection | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2828015/ |
| INS | insulin | increase | pancreas | GLP-1 signaling and the regulation of pancreatic β-cells mass/function | https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-avances-diabetologia-326-articulo-glp-1-signaling-regulation-pancreatic-cells-S1134323011700023 |
| IRS2 | insulin receptor substrate 2 | increase | pancreas | GLP-1 signaling and the regulation of pancreatic β-cells mass/function | https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-avances-diabetologia-326-articulo-glp-1-signaling-regulation-pancreatic-cells-S1134323011700023 |
| MGAT3 | mannosyl (beta-1,4-)-glycoprotein beta-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase | decrease | neurogenesis | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: A Focus on Neurodegenerative Diseases | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6813233/ |
| MTOR | mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase | increase | neurogenesis | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: A Focus on Neurodegenerative Diseases | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6813233/ |
| NEUROG3 | neurogenin-3 | increase | pancreas | Exendin-4 enhances expression of Neurod1 and Glut2 in insulin-producing cells derived from mouse embryonic stem cells | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4754381/ |
| NLRP3 | inflammasome component | decrease | microglia | Anti-Inflammatory Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Activation in the Brain in Neurodegenerative Diseases | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9455625/ |
| NOS1 | nitric oxide synthase 1 | decrease | neurogenesis | Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor stimulation as a means of neuroprotection | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2828015/ |
| NOS2 | nitric oxide synthase 2 | decrease | neurogenesis | Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor stimulation as a means of neuroprotection | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2828015/ |
| NOS3 | nitric oxide synthase 3 | decrease | neurogenesis | Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor stimulation as a means of neuroprotection | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2828015/ |
| NPPA | atrial natriuretic peptide | increase | lung | Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 and Atrial Natriuretic Peptide in a Female Mouse Model of Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32010874/ |
| NPPB | brain natriuretic peptide | decrease | heart | Glucagon-like peptide 1 reverses myocardial hypertrophy through cAMP/PKA/RhoA/ROCK2 signaling | https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmaa038 |
| NTRK2 | neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase 2 | increase | neurogenesis | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: A Focus on Neurodegenerative Diseases | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6813233/ |
| PCK1 | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase | decrease | hepatocytes | Duodenal GLP-1 signaling regulates hepatic glucose production through a PKC-?-dependent neurocircuitry | https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28182013/ |
| PDX1 | pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 | increase | pancreas | GLP-1 signaling and the regulation of pancreatic β-cells mass/function | https://www.elsevier.es/es-revista-avances-diabetologia-326-articulo-glp-1-signaling-regulation-pancreatic-cells-S1134323011700023 |
| POMC | proopiomelanocortin | increase | decrease food intake via hypothalamus | Exendin-4 reduces food intake via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in the hypothalamus | https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-017-06951-0 |
| PPARA | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha | increase | liver | Glucagon like-peptide 1 receptor and the liver | https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1478-3231.2011.02626.x |
| PPARG | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma | increase | liver | Glucagon like-peptide 1 receptor and the liver | https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1478-3231.2011.02626.x |
| PRKAA1 | Protein Kinase AMP-Activated Catalytic Subunit Alpha 1 | increase | hepatocytes | Liraglutide reduces fatty degeneration in hepatic cells via the AMPK/SREBP1 pathway | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4665609/ |
| SLC2A2 | Glucose transporter 2 | increase | pancreas | Exendin-4 enhances expression of Neurod1 and Glut2 in insulin-producing cells derived from mouse embryonic stem cells | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4754381/ |
| SREBF1 | sterol regulatory element binding protein 1 | decrease | hepatocytes | Liraglutide reduces fatty degeneration in hepatic cells via the AMPK/SREBP1 pathway | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4665609/ |
| TFF3 | trefoil factor 3 | decrease | small intestine | GLP-1R Agonists Modulate Enteric Immune Responses Through the Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocyte GLP-1R | https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1577 |
| TNFA | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha | decrease | monocytic cell line | Effect of liraglutide on expression of inflammatory genes in type 2 diabetes | https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-021-97967-0 |
| TNFA | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha | increase | small intestine | GLP-1R Agonists Modulate Enteric Immune Responses Through the Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocyte GLP-1R | https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1582 |