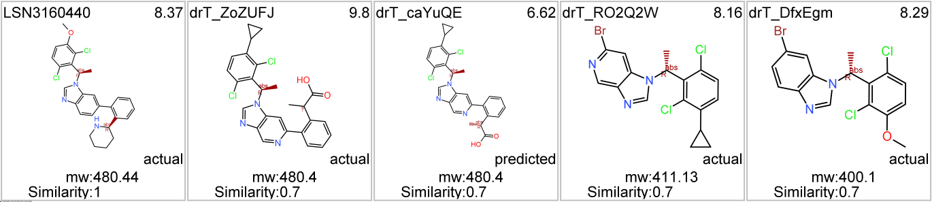
5 compounds from a SAR exercise after a high throughput screening carried out at Lilly have been documented by researchers from Penn State University in ChEMBL DB.
ChEMBL records show activities on GLP1R activation and antidiabetic assays.
ChEMBL results are described in detail in the article below, also heading the treeMap above.
J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2019 Nov;33(11):973-981. DOI: 10.1007/s10822-019-00254-4. PMID: 31758355
Discovery of a potential positive allosteric modulator of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor through virtual screening and experimental study
Tejashree Redij 1, Jian Ma 2, Zhiyu Li 3, Xianxin Hua 2, Zhijun Li 4 5
Abstract
The Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R) is a well-established target for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and GLP-1R agonist-based therapies represent an effective approach which results in several GLP-1 analog drugs. However, the development of nonpeptidic agonist drugs targeting GLP-1R remains unsuccessful. A promising strategy aims to develop orally bioavailable, small-molecule positive allosteric modulators of GLP1-1R. Taking advantage of the recently reported cryo-EM structure of GLP-1R at its active state, we have performed structure-based screening studies which include potential allosteric binding site prediction and in silico screening of drug-like compounds, and conducted in vitro testing and site-specific mutagenesis studies. One compound with low molecular weight was confirmed as a positive allosteric modulator of GLP-1R as it enhances GLP-1’s affinity and efficacy to human GLP-1R in a dose dependent manner. This compound also stimulates insulin secretion synergistically with GLP-1. With the molecular weight of 399, this compound represents one of the smallest known GLP-1R PAMs, and demonstrates other favorable drug-like properties. Site-specific mutagenesis studies confirmed that the binding site of this compound partially overlaps with that of a known antagonist in the transmembrane domain. These results demonstrate that structure-based approach is useful for discovering nonpeptidic allosteric modulators of GLP-1R and the compound reported here is valuable for further drug development.
Keywords: Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor; Positive allosteric modulator; Type-2 diabetes; Virtual screening.
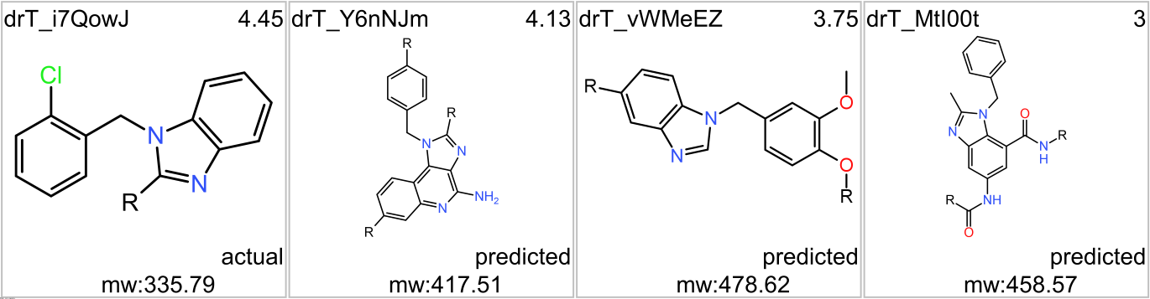
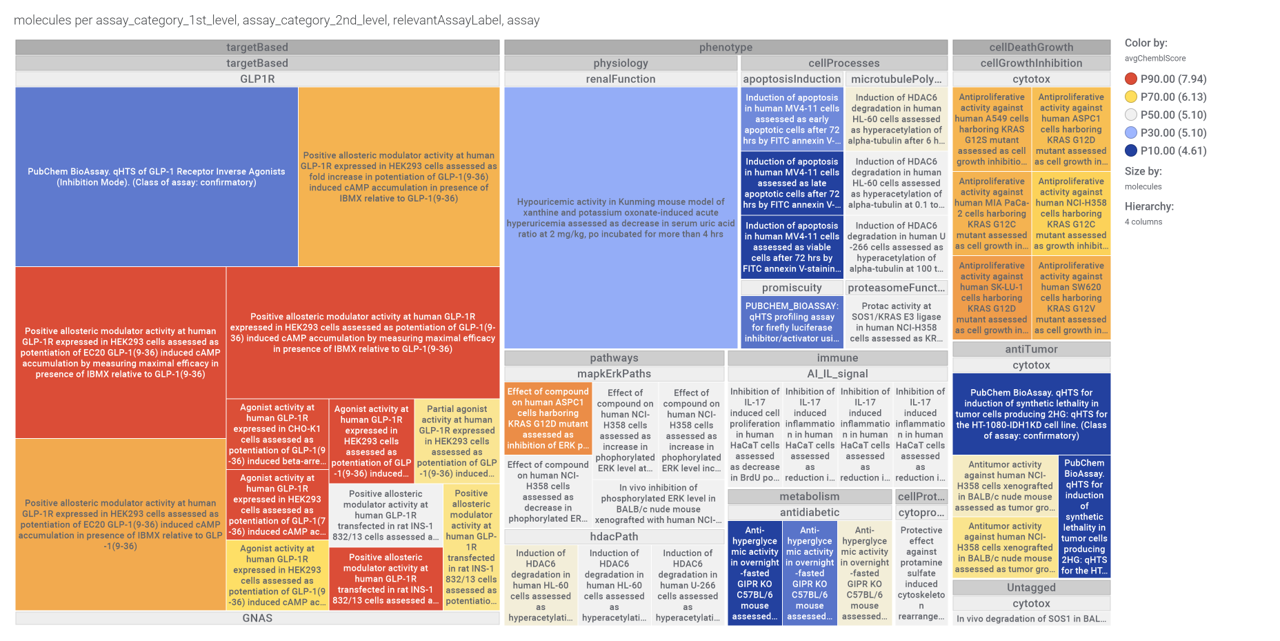
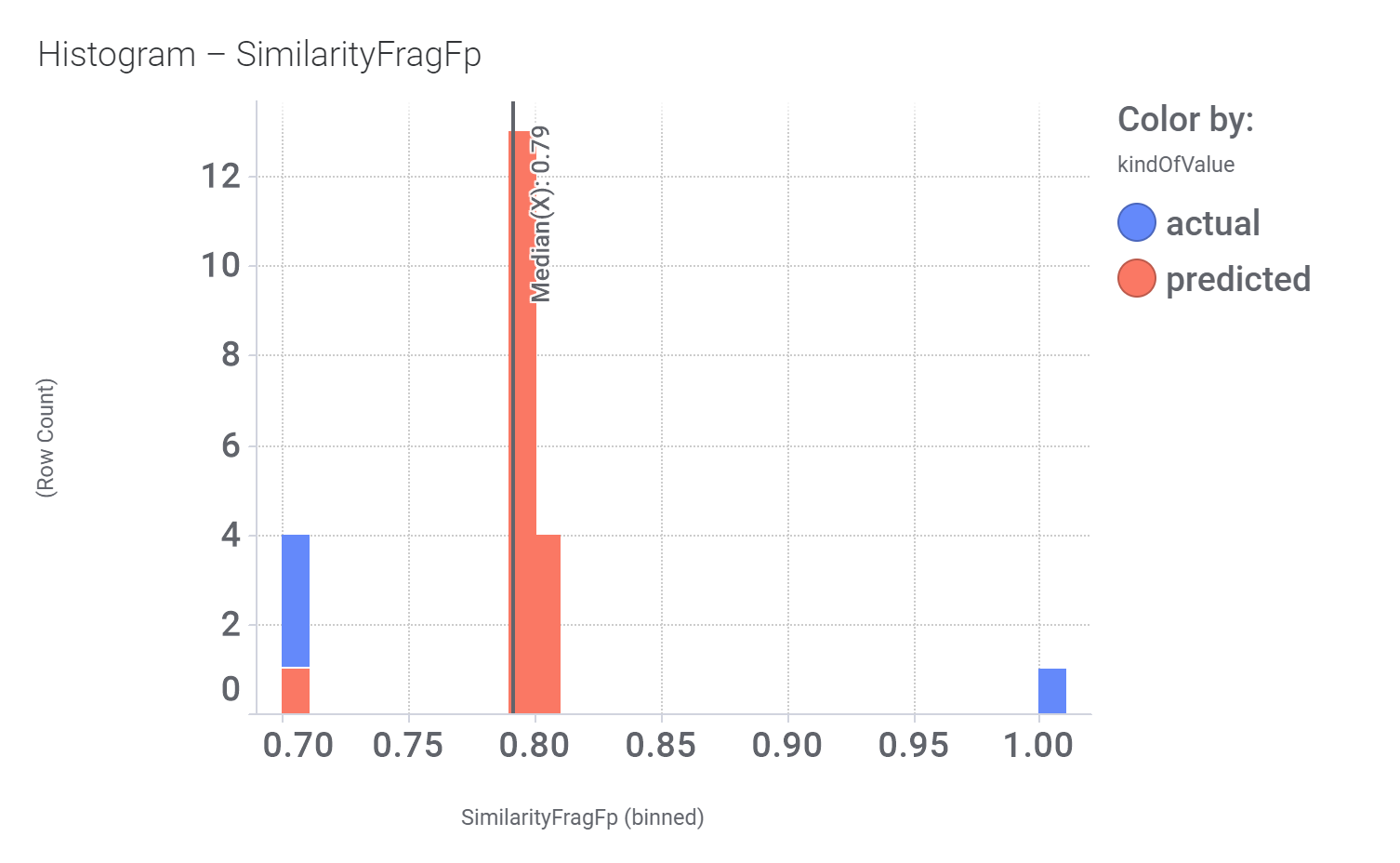
Although no close LSN3160440 analogs have been identified among the predicted 37k GLP1R PAMs, 87 molecules contain the benzimidazoleEthylBenzene scaffold common to Lilly compounds.
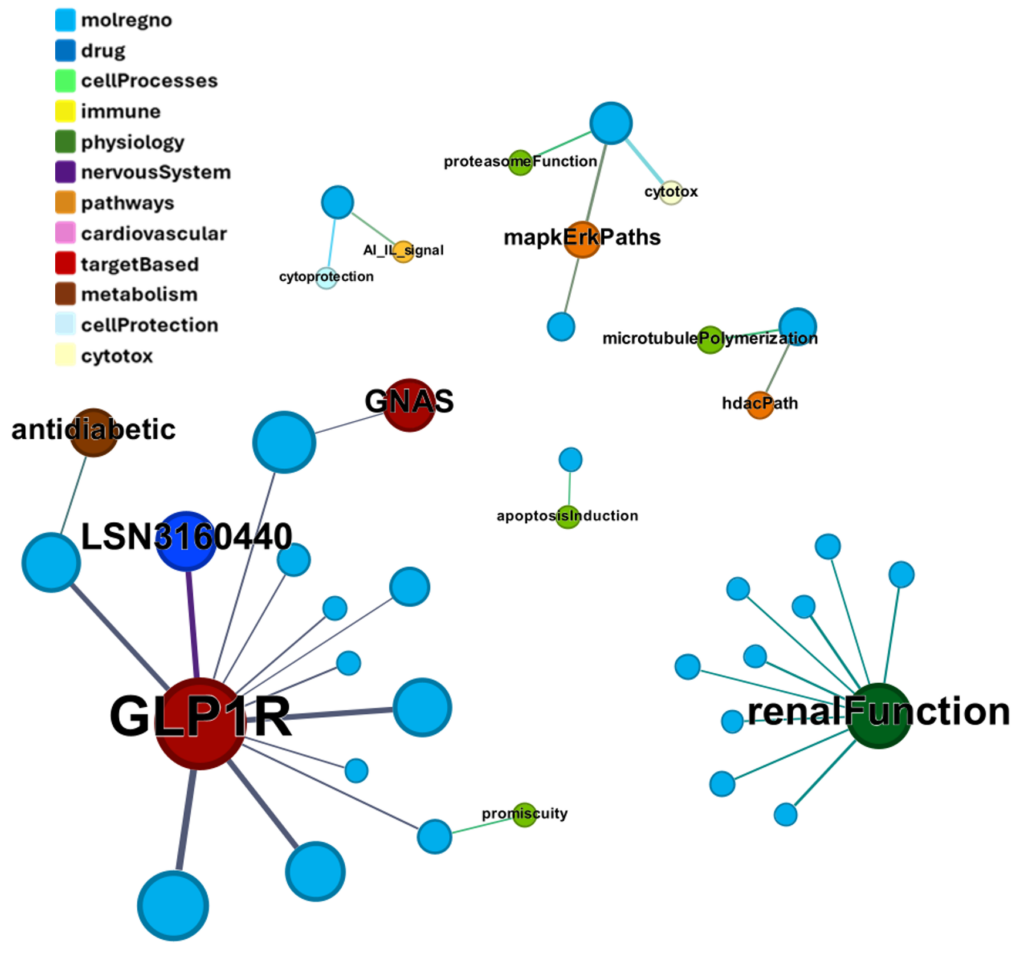
We can visualize most relevant activities of these compounds at ChEMBL using a network graph.
Or a treeMap
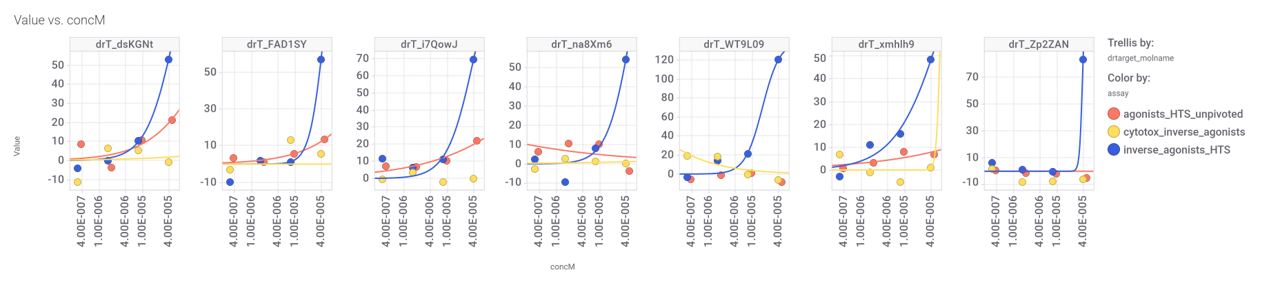
Some of these benzimidazoleEthylbenzenes show activity in GLP1R Pubchem screens.
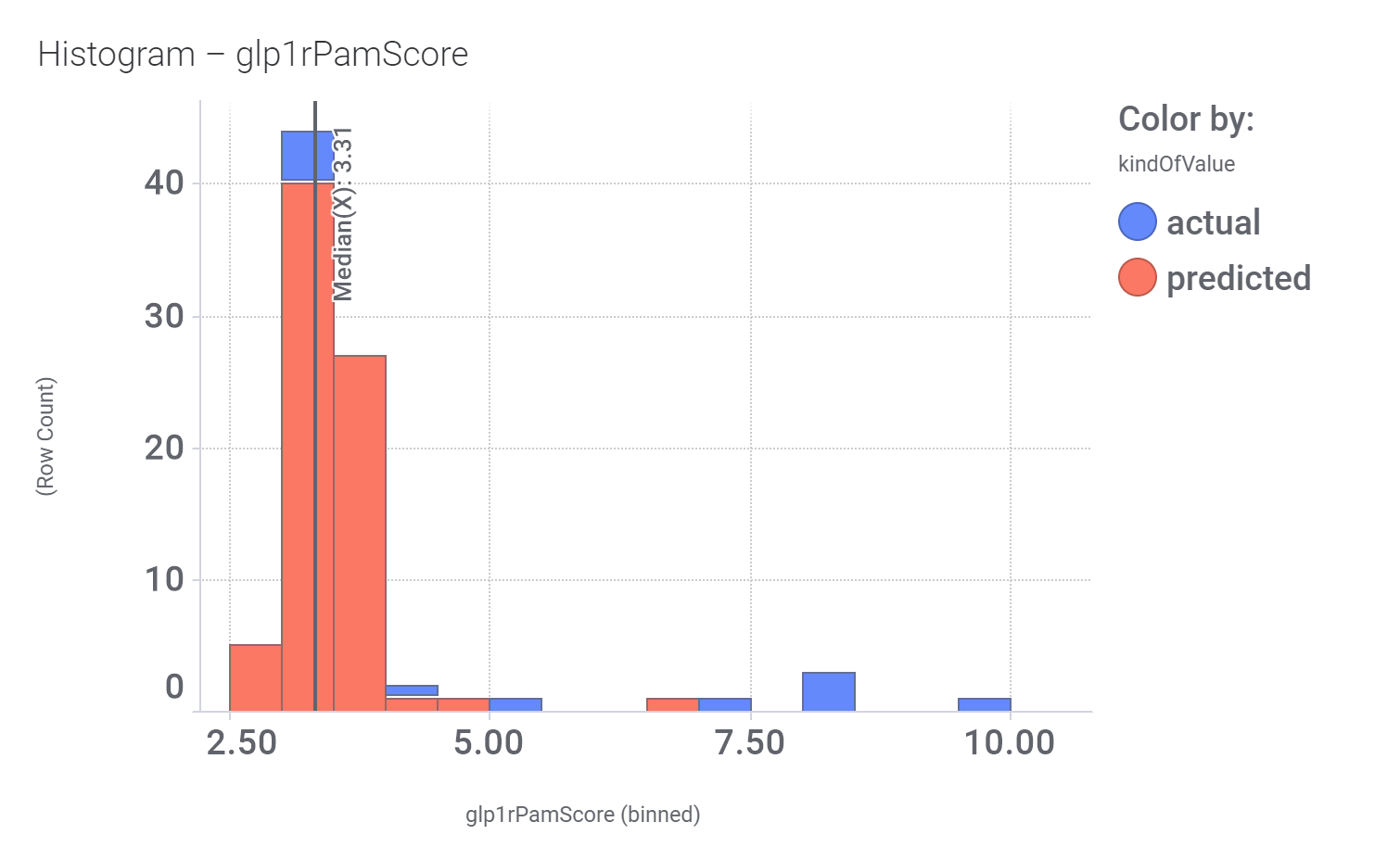
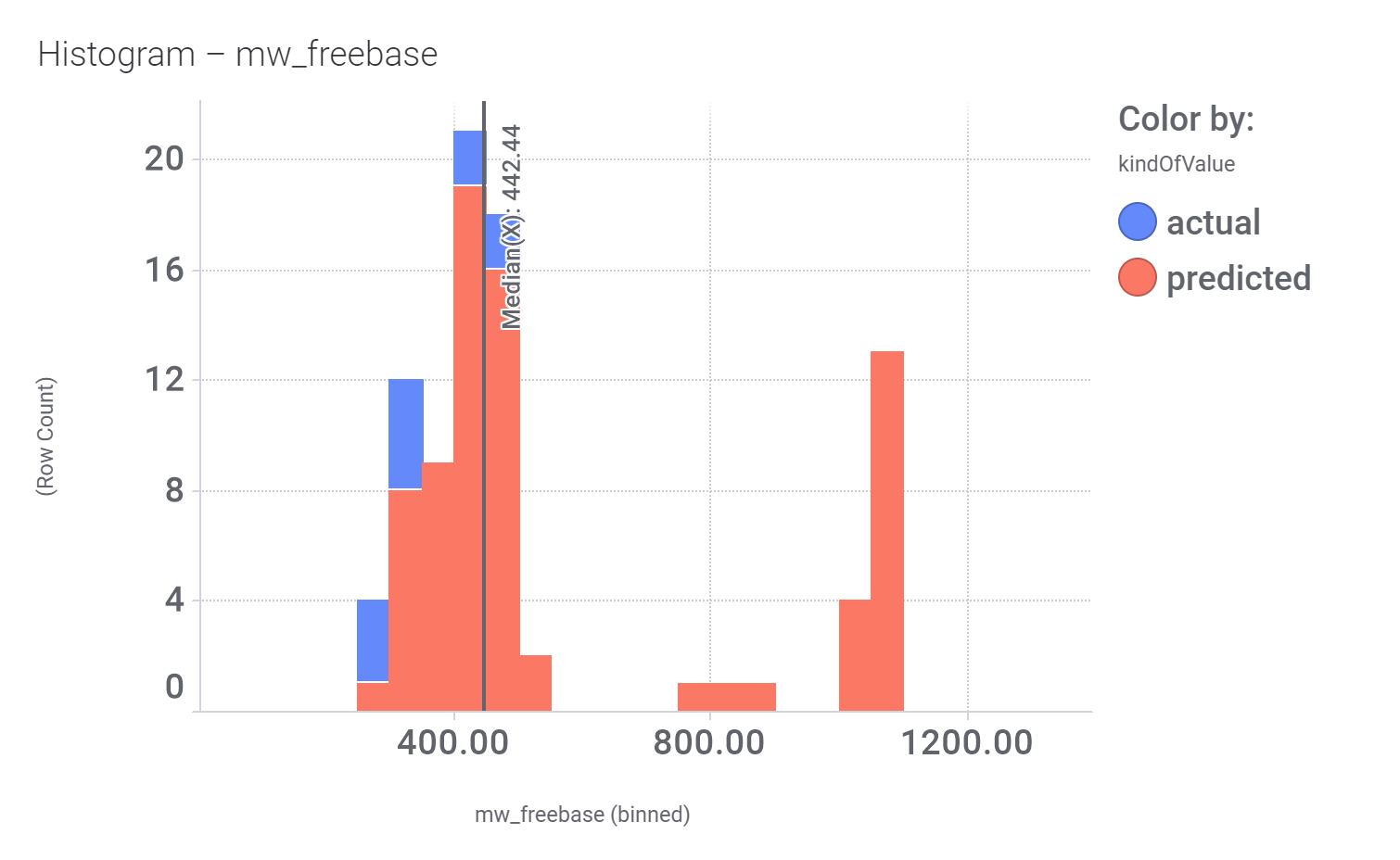
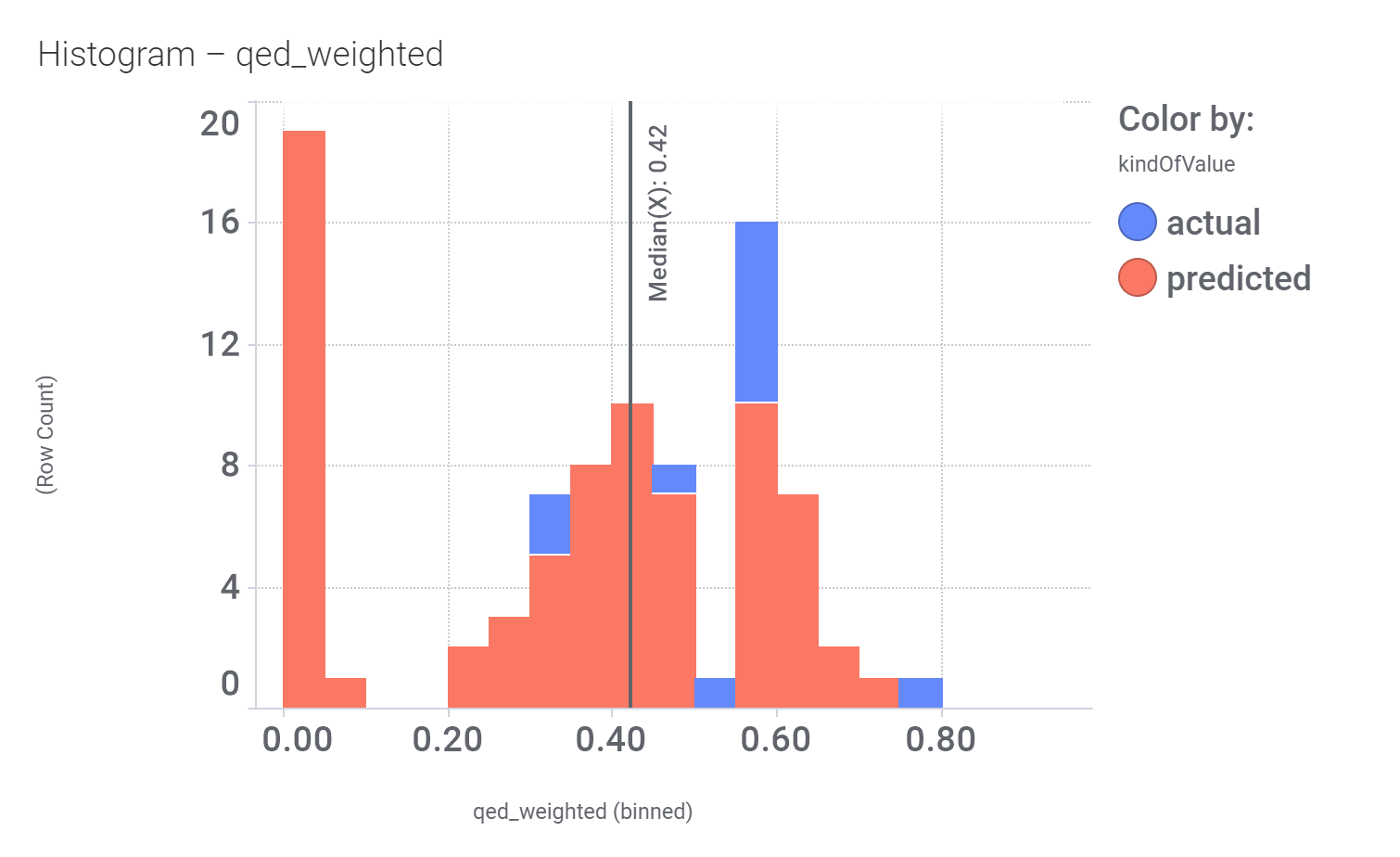
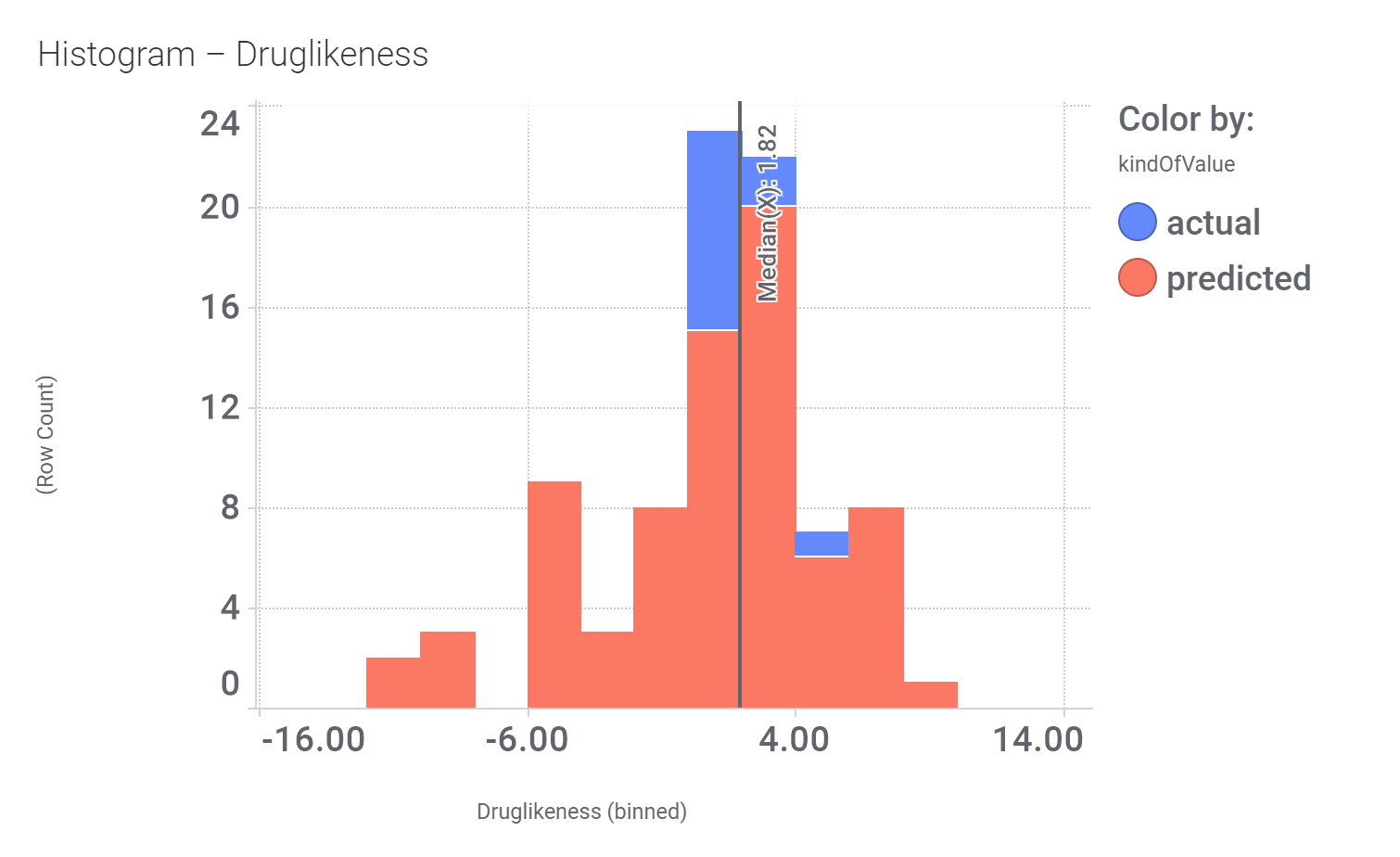
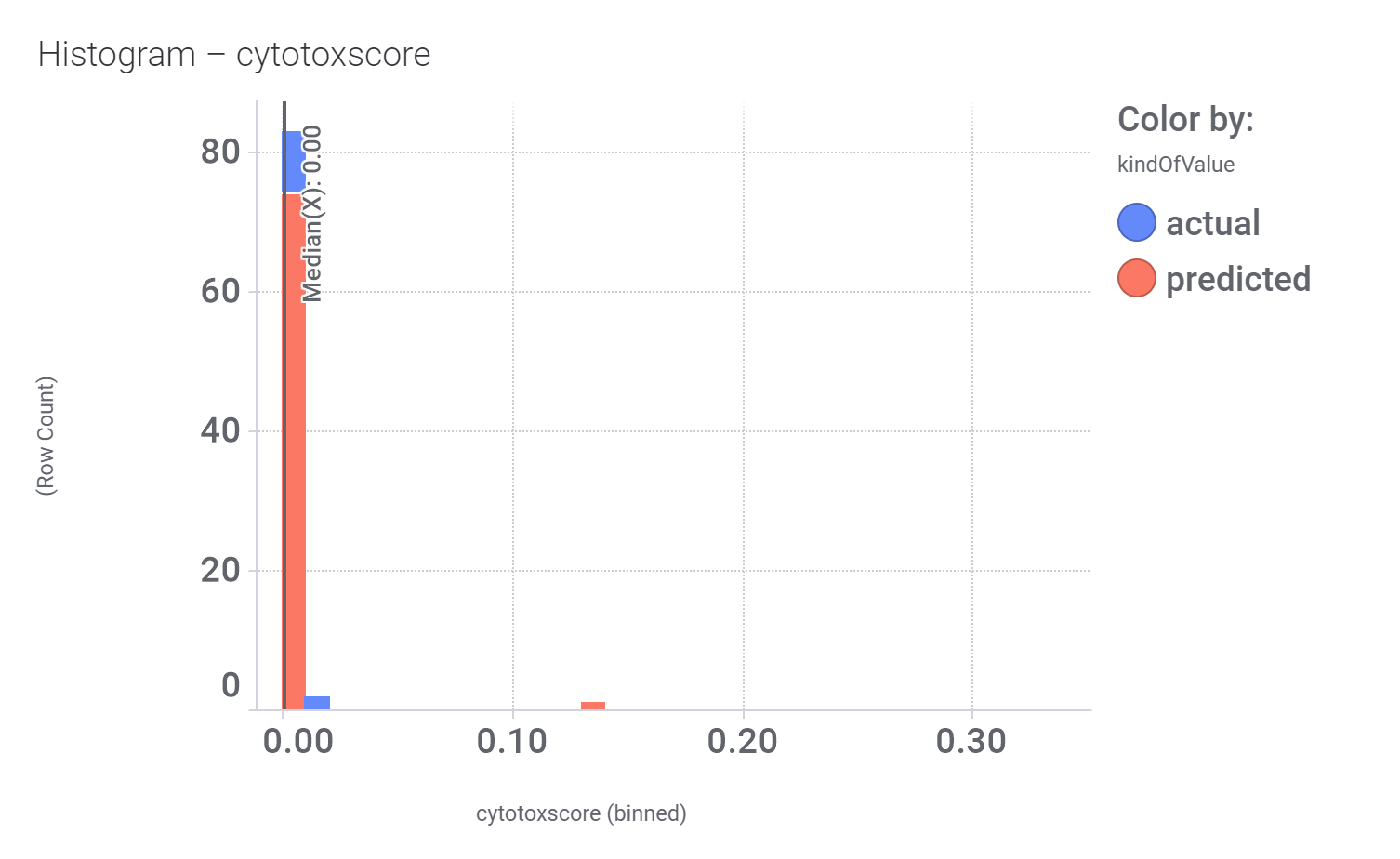
And these are the benzimidazoleEthylbenzenes bio-physicochemical and developability properties
Druglikeness estimated by QedWeighted.
Druglikeness estimated by DataWarrior.
Additional references.
Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Feb; 179(4): 511–525. doi: 10.1111/bph.15446
Non‐peptide agonists and positive allosteric modulators of glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptors: Alternative approaches for treatment of Type 2 diabetes
Faisal Malik 1 and Zhijun Li 1
Abstract
Glucagon‐like peptide‐1 (GLP‐1) receptors belong to the pharmaceutically important Class B family of GPCRs and are involved in many biologically significant signalling pathways. Its incretin peptide ligand GLP‐1 analogues are effective treatments for Type 2 diabetes. Although developing non‐peptide low MW drugs targeting GLP‐1 receptors remains elusive, considerable progress has been made in discovering non‐peptide agonists and positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) of GLP‐1 receptors with demonstrated efficacy. Many of these compounds induce biased signalling in GLP‐1 receptor‐mediated functional pathways. High‐quality structures of GLP‐1 receptors in both inactive and active states have been reported, revealing detailed molecular interactions between GLP‐1 receptors and non‐peptide agonists or PAMs. These progresses raise the exciting possibility of developing non‐peptide drugs of GLP‐1 receptors as alternative treatments for Type 2 diabetes. The insight into the interactions between the receptor and the non‐peptide ligand is also useful for developing non‐peptide ligands targeting other Class B GPCRs.
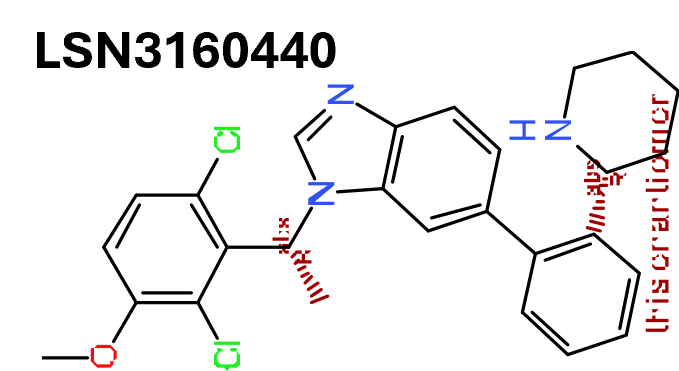
3.1.9. LSN3160440
In another effort to take advantage of endogenous GLP‐1(9–36)NH2, the group at Eli Lilly and Company performed the screening of a diverse 220,000 compound library using the HEK293 cells expressing human GLP‐1 receptors, in the presence of a 20%‐maximum effective concentration (EC20) of GLP‐1(9–36). The screening led to the discovery of a known MET kinase inhibitor as a weak potentiator of GLP‐1 receptors (Bueno et al., 2020). Multiple rounds of SAR optimization were conducted on this lead compound which resulted in the discovery of compound 15 (LSN3160440) (Figure 3, [15]). In vitro, LSN3160440 enhanced the potency and efficacy of GLP‐1(9–36) in GLP‐1 receptor‐induced cAMP signalling. Competitive binding studies indicated LSN3160440 cooperatively modulated the binding affinity and efficacy of GLP‐1(9–36) for GLP‐1 receptor activation. LSN3160440 is selective against MET and 33 other diverse kinases, as well as 261 GPCRs. LSN3160440 also exhibits strong probe dependence, being a robust potentiator of GLP‐1(9–36) but not oxyntomodulin or full‐length GLP‐1.
In pancreatic islets from mice, LSN3160440 combined with GLP‐1(9–36) significantly increases glucose‐dependent insulin secretion to the levels comparable to that produced by full‐length GLP‐1. In vivo characterization using Wistar rats indicated that the combination of LSN3160440 and GLP‐1(9–36) elicits an insulinotropic effect similar to that produced by full‐length GLP‐1.
The cryo‐EM structure of GLP‐1 receptors bound to LSN3160440, GLP‐1 and Gs protein was solved which indicates LSN3160440 binds at the extracellular side of the helical bundle in a pocket formed by residues in the interface between TM1 and TM2 (Figure 4) (Bueno et al., 2020). In the complex structure, LSN3160440 interacts with both GLP‐1 peptide and GLP‐1 receptor simultaneously. The 2,6‐dichloro‐3‐methoxyl phenyl moiety of LSN3160440 forms van der Waals (vdW) contacts with the GLP‐1 peptide and the benzimidazole of LSN3160440 forms vdW interactions and π–π stacking with the GLP‐1 receptor. LSN3160440 is likely to be the only reported PAM for a receptor that mediates its positive allostery through simultaneous interactions with both the orthosteric ligand and the receptor. Reciprocal site‐specific mutagenesis studies demonstrate that one varied amino acid between GLP‐1(9–36) and oxyntomodulin, V16 of GLP‐1 and Y10 of oxyntomodulin, confers probe dependency on LSN3160440. The discovery of LSN3160440 and its unique binding mode indicates that developing stabilizers at protein–protein interface to affect cell surface signalling can be achieved.
Nat Chem Biol. 2020 Oct;16(10):1105-1110. PMID: 32690941. DOI: 10.1038/s41589-020-0589-7
Structural insights into probe-dependent positive allosterism of the GLP-1 receptor
Ana B Bueno # 1, Bingfa Sun # 2, Francis S Willard # 3, Dan Feng 2, Joseph D Ho 4, David B Wainscott 3, Aaron D Showalter 5, Michal Vieth 4, Qi Chen 6, Cynthia Stutsman 5, Betty Chau 4, James Ficorilli 5, Francisco J Agejas 1, Graham R Cumming 1, Alma Jiménez 1, Isabel Rojo 1, Tong Sun Kobilka 2, Brian K Kobilka 7, Kyle W Sloop 8
Abstract
Drugs that promote the association of protein complexes are an emerging therapeutic strategy. We report discovery of a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) ligand that stabilizes an active state conformation by cooperatively binding both the receptor and orthosteric ligand, thereby acting as a ‘molecular glue’. LSN3160440 is a positive allosteric modulator of the GLP-1R optimized to increase the affinity and efficacy of GLP-1(9-36), a proteolytic product of GLP-1(7-36). The compound enhances insulin secretion in a glucose-, ligand- and GLP-1R-dependent manner. Cryo-electron microscopy determined the structure of the GLP-1R bound to LSN3160440 in complex with GLP-1 and heterotrimeric Gs. The modulator binds high in the helical bundle at an interface between TM1 and TM2, allowing access to the peptide ligand. Pharmacological characterization showed strong probe dependence of LSN3160440 for GLP-1(9-36) versus oxyntomodulin that is driven by a single residue. Our findings expand protein-protein modulation drug discovery to uncompetitive, active state stabilizers for peptide hormone receptors.